What is root cause analysis?
Root cause analysis (RCA) locates a problem's origin and looks for ways to address it. RCA helps businesses and experts concentrate on the root of an issue rather than its symptoms.
RCA investigates an incident's causal factors, concentrating on what, why, and when. An organization often starts an RCA to determine the primary cause of a problem and to stop it from happening again.
RCA uncovers the challenges an organization needs to address and helps them develop better strategies to achieve goals and improve processes. Companies save on cost, avoid recurring issues, and mitigate risks associated with processes through a root cause analysis. For instance, a security incident may require an incident response team to perform an RCA using network management software to understand who was using the system during the incident.
Types of causes for root cause analysis
RCA assumes a relationship between systems and events. The effects of one action radiate out to affect others, and so on. Different types of issues require RCA, but the triggers for RCA usually fall into three categories:l.
- Physical causes refer to tangible issues like equipment failures, machinery malfunctions, or infrastructure problems.
- Human causes are simply mistakes or errors made by people. They could result from not following procedures correctly, lack of training, or miscommunication.
- Organizational causes stem from the overall structure, policies, or organization’s culture. It could include inadequate resources, poor decision-making processes, or ineffective leadership.
Root cause analysis methods
Organizations perform RCA through multiple techniques depending on the problem, preference, and field.
- The Five Whys is a simple method to find the root cause of a problem by asking "why" repeatedly. In this way, businesses can dig deeply and uncover the real reason behind an issue. The goal is to keep questioning until the true cause and its solution are determined.
- A fishbone diagram looks like a fish skeleton, and is sometimes referred to as a Fishikawa or Herringbone diagram, or plainly, a cause-and-effect diagram.
- Failure mode and effects analyses (FMEA) evaluate past data to predict future failures and defects in a machine or system. It involves three main components: quality control efforts, safety engineering, and reliability engineering.
- Pareto charts combine bar charts and line graphs to identify the most significant causes of a problem with multiple causes. The causes are shown as bars in descending order of importance, and a line graph shows their cumulative business impact. The Pareto chart is based on the 80/20 Rule, suggesting that 80% of problems result from 20% of the causes.
Benefits of root cause analysis
Root cause analysis is beneficial for businesses from diverse sectors. Here are a few notable RCA advantages:
- Simplicity and versatility. This technique is easy to understand and most businesses can implement it quickly.
- Complexity handling. For more complex problems, businesses can use the five whys method. It allows them to identify and address multiple root causes.
- Long-term problem resolution. Organizations can prevent problems from recurrence by addressing the root causes, boosting overall efficiency.
The process of root cause analysis
Organizations work cross-functionally to conduct the analysis. If the issue affects many teams, gather a group of staff members from each concerned team.
- Identify the problem. Define the problem and understand its symptoms. It could be a mistake made by a person, a malfunctioning machine, or a flawed process. Look for any factors contributing to it while searching for the root cause.
- Collect data. Once the organization identifies the problem, gain as much information as possible. This includes talking to everyone involved, collecting screenshots and logs, and reviewing incident reports.
- Determine possible causes. Find the significant factors that led to the problem. Create a timeline of events to identify the specific causes and any other related issues. Doing so helps understand which factors are responsible for the problem.
- Find the root cause. Work with the team to brainstorm and find the root cause. Use techniques like Pareto charts and Fishbone diagrams to analyze the leading underlying cause. It's essential to have a collaborative approach and avoid blaming each other.
- Implement the solution. Come up with potential solutions, evaluate the best ones, and decide when to implement them. After setting up the solution, monitor it closely to ensure its efficiency and accuracy.
- Document the actions. Document the issue, solution, and preventive actions to prevent it from happening again.
Objectives of root cause analysis
Root cause analysis experts who want to continuously improve reliability should be able to employ the most appropriate technique. An RCA has three primary objectives:
- Determine the exact nature of the problem. Look at the actual course of events and the underlying causes and symptoms.
- Recognize the necessary next steps. Address the occurrence and what teams have gained from mistakes.
- Use the learned steps. Replicate the underlying circumstances or stop the issue from happening again.
Best practices of root cause analysis
Communication is the key to RCA. Stakeholders must be aware of the timeframes of incidental or related factors, their consequences, and the resolution techniques.
- Find out what or who caused the incident. From there, companies can determine how and when it happened. These inquiries paint a thorough picture of the main issues. For instance, if businesses don't know how or when something happened, it is challenging to determine why.
- When using RCA to solve issues, consider prevention. Locating the source of an issue isn’t enough to count as success., An RCA must also allow for the implementation of solutions that stop the issue from happening again.
- Get it correct the first time. An RCA is only as good as the work that goes into it. A poor RCA could be a waste of time and resources. It can make things worse, prompting investigators to reopen the case.
Root cause analysis vs. gap analysis
It's common to confuse root cause analysis with a gap analysis, but the two are very different.
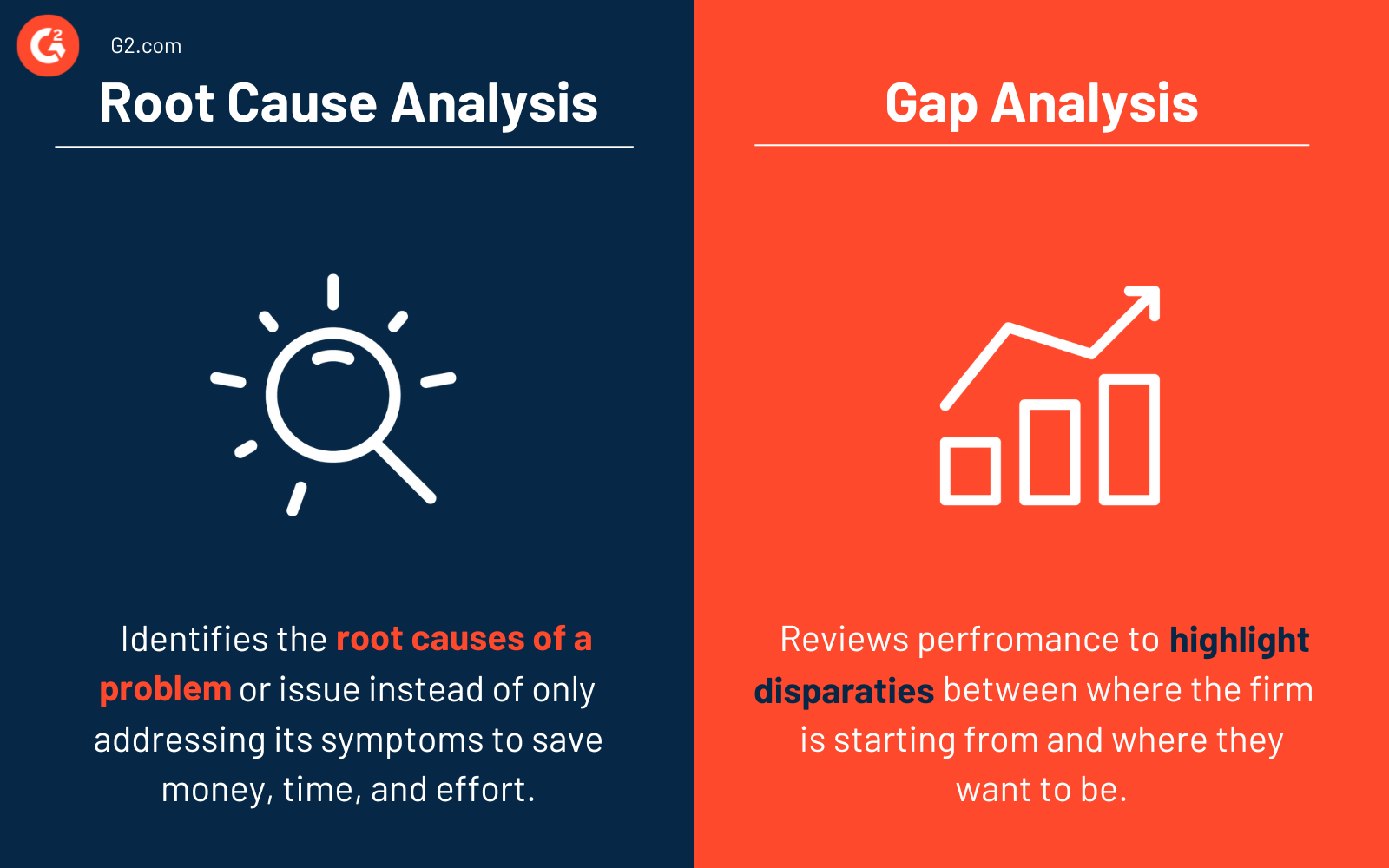
Root cause analysis identifies the root causes of a problem or issue instead of only addressing its symptoms. Businesses use this technique to stop the issue from reoccurring and enhance the service or process by finding the leading causes. Using RCA properly saves money, time, and effort.
Gap analysis reviews and evaluates the business’s performance to highlight the disparities between where the firm is starting from and where they want to be. Businesses employ gap analysis to evaluate their current performance and goals. This evaluation helps a business see if it’s spending its resources wisely and meeting customer expectations.
Take your knowledge one step further by learning about log analysis and its benefits.

Sagar Joshi
Sagar Joshi is a former content marketing specialist at G2 in India. He is an engineer with a keen interest in data analytics and cybersecurity. He writes about topics related to them. You can find him reading books, learning a new language, or playing pool in his free time.